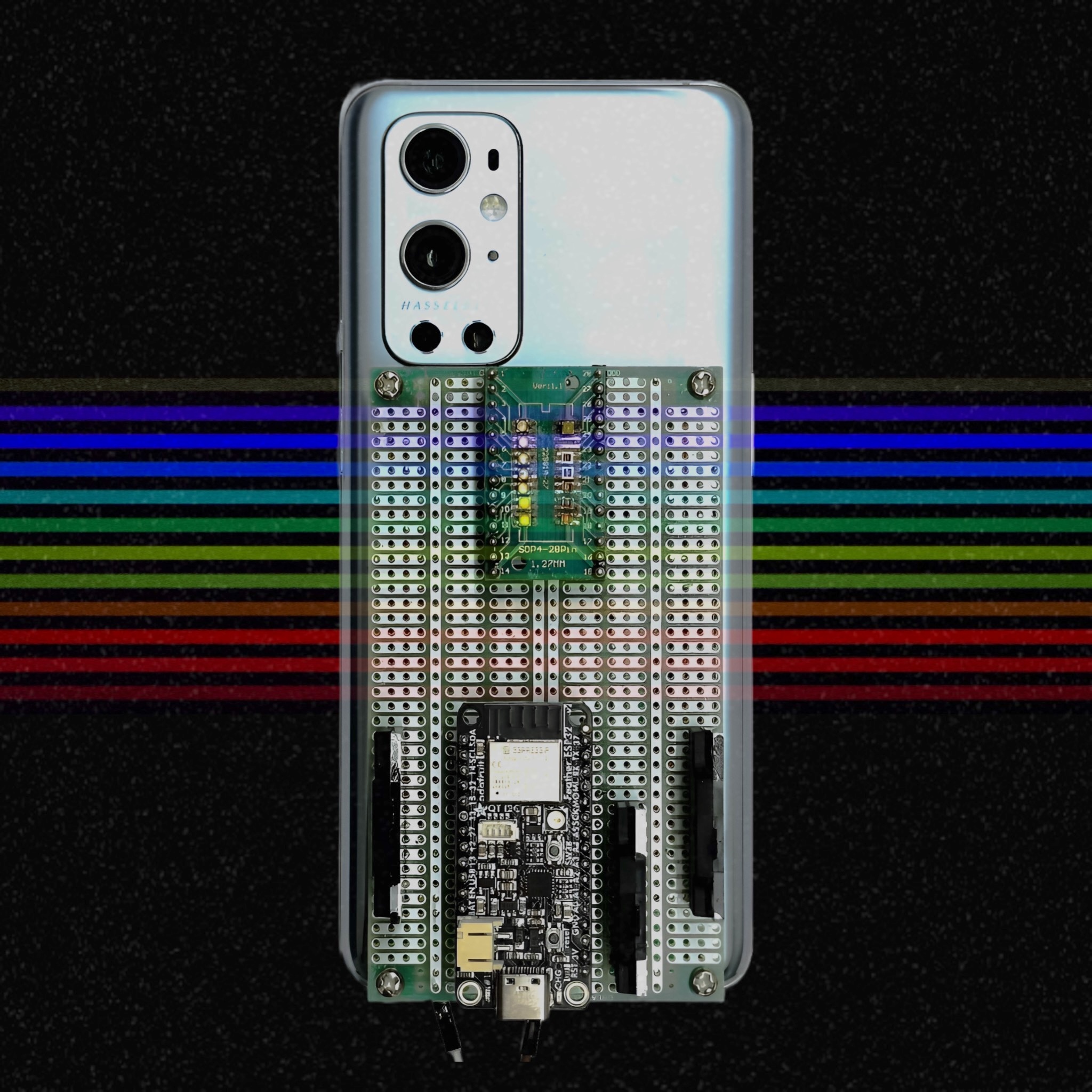
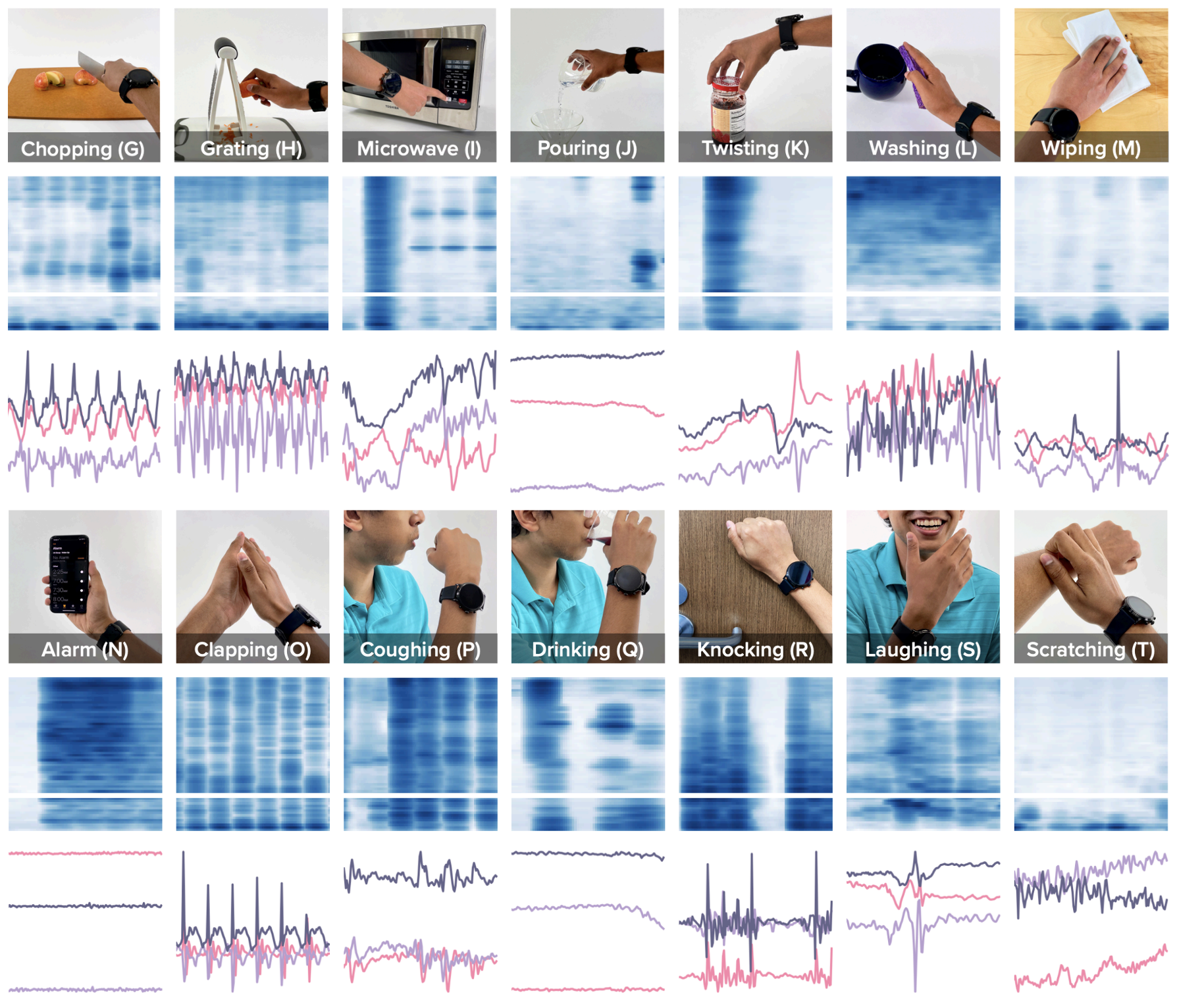
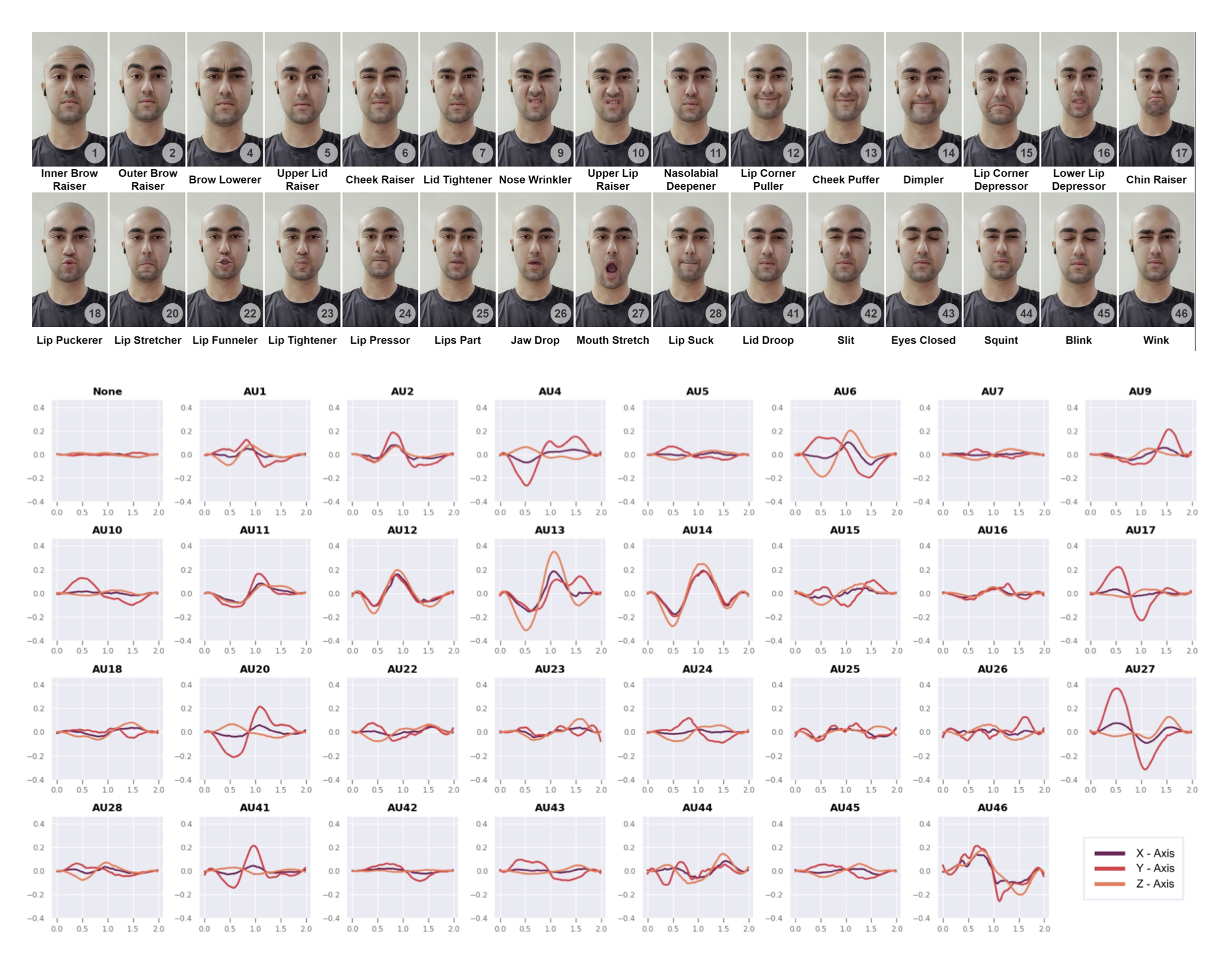
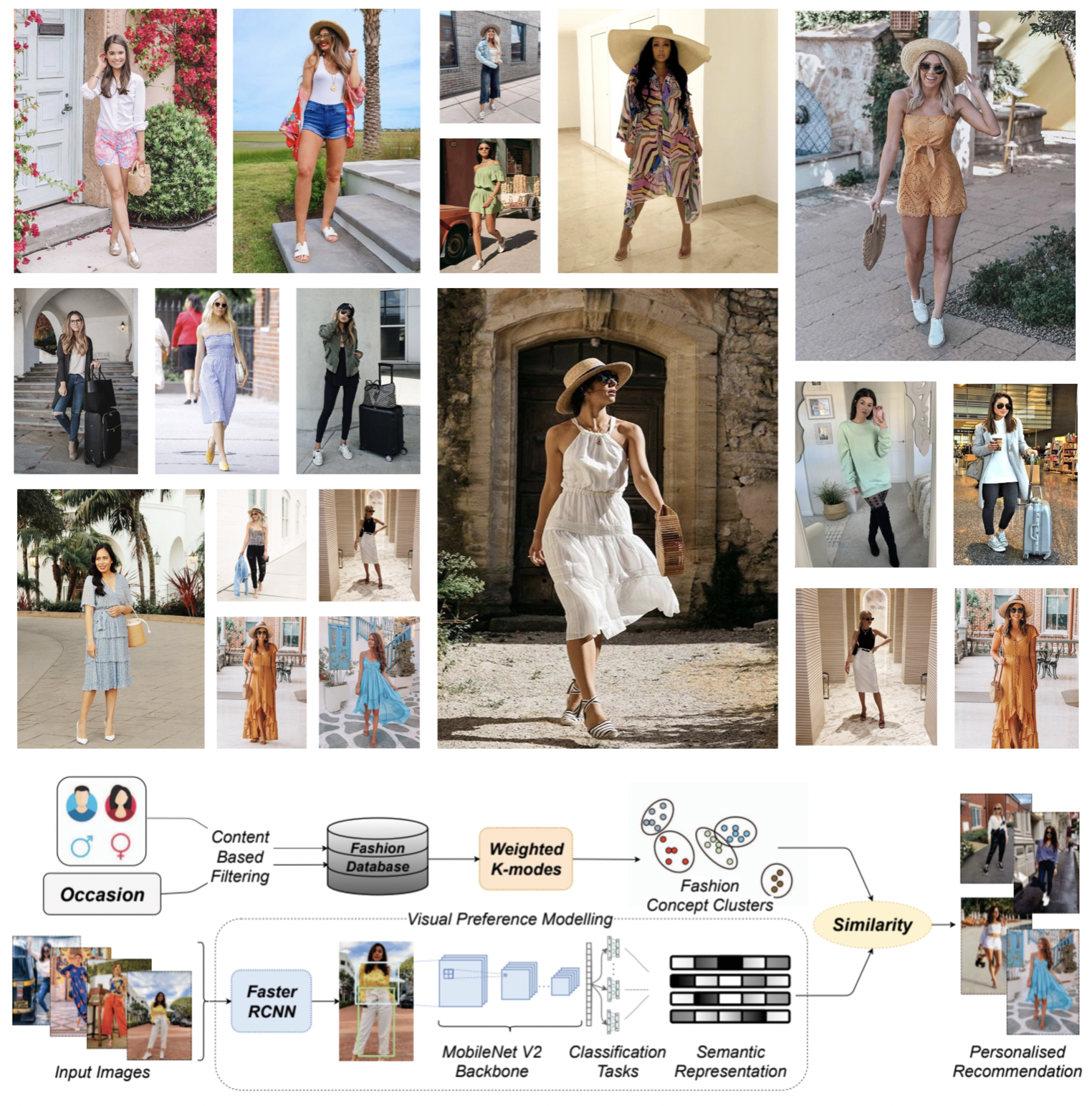
Namaste!
I'm Dhruv Verma
I'm a Ph.D. student at the University of Toronto, advised by Prof.
Alex Mariakakis.
Broadly, my research involves advancing the capabilities of computing devices to
sense and perceive information (inertial, visual, acoustic, physiological,
and others) relevant to understanding the human body, behaviour and the surrounding context.
During my doctoral journey, I've developed a keen interest in
computational imaging.
Specifically, in building computing infrastructure that leverages ubiquitous devices to
provide a visual perspective of the world that extends beyond human perception. In realizing
these systems, I bring together my expertise in signal and image processing, engineering,
and machine learning with a human-centred approach at the core.
My endeavours are driven by a desire to unlock new possibilities and improve existing tasks enabled by
sensing systems, particularly those focused on improving health outcomes and enhancing human-computer interaction.
Update: I'm seeking research internships for 2025. If you're recruiting and think I'd be a good fit, please don't hesitate to reach out!